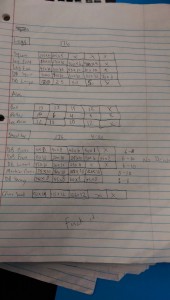
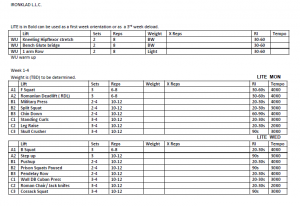
General Rules and Guidelines for a diet:
Weight in the morning daily for feedback (1)
-Eat Fats and Proteins in the morning, eat Carbohydrates and Proteins at night (2) (20)(21)
-The lower levels of visceral body fat the better the body assimilates carbs (3)
-Fibers provide satiety and doesn’t count towards carbs (4)
-There is a link between protein “deficiency” and increase caloric intake (5)
-Whey protein intake adds to satiety (6)
-Diet Soda and Diet sweeteners can create cravings for sweets (7)
-There is some benefit to consumption of acids with higher carbohydrate meal. (8)
-Adequate sleep is required for optimal carbohydrate assimilation (9)(10)
-glycemic load will dictate satiety throughout the day (11)
-increased protein intake will help maintain lean body mass on a diet (12)
-High protein low fat diet in some ways is superior to high carb diets (13)
– Aerobics in conjunction with weight training helps maintain lean body mass when in caloric deficit (14)
– 7 day 15g per per kg of body mass to fully replete glycogen stores (15)
-When hungry err on the side of higher protein (16)
– The body can and does assimilate nutrients after a workout similar to a fasted state (17)(18)(19)
-High Protein Breakfast benefits satiety and prevents BF gain (22)
– Sleep Deprivation and metabolic function and immunity (23)(26)
– A routine meal pattern may help with thermic effect of food along with weight management (24)(25)
(1)http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16336072
(2)http://www.strengthsensei.com/the-case-for-eating-your-carbohydrates-at-night/
(3) http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00125-003-1074-z
(4) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25823991
(5) http://www.jci.org/articles/view/74915
(6) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25563737
(7) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2892765/
(8) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16015276
(9) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25870289
(10) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19255424
(11)http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3762696/
(12) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19927027
(13) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15941879
(14) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10487375
(15)http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/48/2/240.abstract
(16) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23067428
(17) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3577439/
(18) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16051710
(19) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19837871
(20) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21475137
(21) http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/85/4/981.short
(22) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26239831
(23) http://www.lf1.cuni.cz/data/files/praguemedicalreport/pmr_109_2008_04/pmr_04-2008_275.pdf
(24) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27305952
(25) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15640455
(26) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10468992